Difference between revisions of "Exemple de base lttoolbox"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Création de la page) |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 07:18, 11 May 2012
Exemple de base
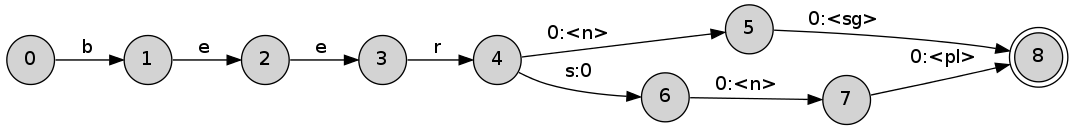
Voici une version simple C++/lttoolbox du programme 'beer' mentionné dans la page Dictionnaire morphologique.
// g++ -I/usr/local/include/lttoolbox-3.2 -I/usr/local/lib -llttoolbox3 lt_beer.cc -o lt-beer
#include <cwchar>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cerrno>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <set>
#include <lttoolbox/ltstr.h>
// LtLocale::tryToSetLocale()
#include <lttoolbox/lt_locale.h>
// Classe Transducer
#include <lttoolbox/transducer.h>
// Classe Alphabet
#include <lttoolbox/alphabet.h>
// Classe State
#include <lttoolbox/state.h>
// Classe TransExe
#include <lttoolbox/trans_exe.h>
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
Alphabet alphabet;
Transducer t;
// Set locale
LtLocale::tryToSetLocale();
// Insérer les symboles dans alphabet, on garde les valeurs
alphabet.includeSymbol(L"<n>");
alphabet.includeSymbol(L"<sg>");
alphabet.includeSymbol(L"<pl>");
int n_sym = alphabet(L"<n>");
int sg_sym = alphabet(L"<sg>");
int pl_sym = alphabet(L"<pl>");
// Etat initial
int initial = t.getInitial();
// construire "beer" à la main
int beer = initial;
// il y a les transitions b:b e:e e:e r:r
beer = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L'b',L'b'), beer);
beer = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L'e',L'e'), beer);
beer = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L'e',L'e'), beer);
beer = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L'r',L'r'), beer);
// il y a 0:<n> 0:<sg>
beer = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(0, n_sym), beer);
beer = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(0, sg_sym), beer);
t.setFinal(beer);
// construire "beers" à la main
int beers = t.getInitial();
beers = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L'b',L'b'), beers);
beers = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L'e',L'e'), beers);
beers = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L'e',L'e'), beers);
beers = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L'r',L'r'), beers);
// cette transition est s:0
beers = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L's', 0), beers);
beers = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(0, n_sym), beers);
beers = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(0, pl_sym), beers);
t.setFinal(beers);
t.minimize();
// Plutôt que d'essayer de convertir entre Transducer et TransExe, on va
// juste écrire et lire
FILE* fst=fopen("beer.fst", "w");
t.write(fst);
fclose(fst);
fst=fopen("beer.fst", "r");
TransExe te;
te.read(fst, alphabet);
fclose(fst);
State *initial_state = new State();
initial_state->init(te.getInitial());
State current_state = *initial_state;
wstring input, output=L"";
set<Node *> anfinals;
anfinals.insert(te.getFinals().begin(), te.getFinals().end());
FILE* in=stdin;
bool reading=true;
// C'est notre exécution : voir si l'entrée est reconnue
while (reading)
{
wchar_t val = (wchar_t)fgetwc(in);
if(val==WEOF||iswspace(val))
{
reading=false;
}
else
{
if (!reading)
{
// A la fin. on n'a pas besoin de faire quoique ce soit
// mais quitter la boucle dans cet exemple simplistelike thi
break;
}
else
{
current_state.step(val);
alphabet.getSymbol(input, val);
}
}
}
if (current_state.isFinal(anfinals))
{
// Non utilisé, on veut juste que ce ne soit pas vide...
set<wchar_t> escaped;
escaped.insert(L'$');
output = current_state.filterFinals(anfinals, alphabet, escaped);
wcout << input << output << endl;
}
else
{
wcout << L"Unrecognised: " << input << endl;
}
return 0;
}
on peut simplifier la construction des transducteurs comme ceci :
// construire "beer" à la main int beer = initial; // il y a les transitions b:b e:e e:e r:r beer = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L'b',L'b'), beer); beer = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L'e',L'e'), beer); beer = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L'e',L'e'), beer); beer = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L'r',L'r'), beer); int beersg = beer; // il y a 0:<n> 0:<sg> beersg = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(0, n_sym), beersg); beersg = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(0, sg_sym), beersg); t.setFinal(beersg); // construire "beers" à la main int beerpl = beer; beerpl = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(L's', 0), beerpl); beerpl = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(0, n_sym), beerpl); beerpl = t.insertSingleTransduction(alphabet(0, pl_sym), beerpl); t.setFinal(beerpl);
Écriture/lecture de plusieurs transducteurs dans le même fichier
// g++ -o test test.cc -I/home/fran/local/include/lttoolbox-3.2 -L/home/fran/local/lib -llttoolbox3
#include <cwchar>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <lttoolbox/ltstr.h>
#include <lttoolbox/lt_locale.h>
#include <lttoolbox/transducer.h>
#include <lttoolbox/alphabet.h>
#include <lttoolbox/regexp_compiler.h>
#include <lttoolbox/compression.h>
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
map<int, Transducer> patterns;
Alphabet a;
RegexpCompiler re;
LtLocale::tryToSetLocale();
FILE *output = stdout;
FILE *fst = fopen(argv[1], "w+");
// Construire les transducteurs
a.includeSymbol(L"<n>");
re.initialize(&a);
re.compile(L"foo");
patterns[1] = re.getTransducer();
re.initialize(&a);
re.compile(L"bar");
patterns[2] = re.getTransducer();
re.initialize(&a);
re.compile(L"baz");
patterns[3] = re.getTransducer();
// Écrire dans les transducteurs
a.write(fst);
Compression::multibyte_write(patterns.size(), fst);
fwprintf(output, L"Patterns: %d, Alphabet: %d\n", patterns.size(), a.size());
for(map<int, Transducer>::iterator it = patterns.begin(); it != patterns.end(); it++)
{
wchar_t buf[50];
memset(buf, '\0', sizeof(buf));
swprintf(buf, 50, L"%d", it->first);
wstring id(buf);
fwprintf(output, L"= %S =============================\n", id.c_str());
it->second.show(a, output);
Compression::wstring_write(id, fst);
it->second.write(fst);
}
fclose(fst);
fwprintf(output, L"\n\n");
// Maintenant lire dans les transducteurs ce qu'on y a écrit, morceau par morceau.
FILE *new_fst = fopen(argv[1], "r");
Alphabet new_alphabet;
map<wstring, Transducer> transducers;
new_alphabet.read(new_fst);
int len = Compression::multibyte_read(new_fst);
while(len > 0)
{
int len2 = Compression::multibyte_read(new_fst);
wstring name = L"";
while(len2 > 0)
{
name += static_cast<wchar_t>(Compression::multibyte_read(new_fst));
len2--;
}
transducers[name].read(new_fst);
len--;
}
fwprintf(output, L"Patterns: %d, Alphabet: %d\n", transducers.size(), new_alphabet.size());
for(map<wstring, Transducer>::iterator it = transducers.begin(); it != transducers.end(); it++)
{
fwprintf(output, L"= %S =============================\n", it->first.c_str());
it->second.minimize();
it->second.show(a, output);
}
fclose(new_fst);
return 0;
}
Utilisation d'expressions régulières
/*
* g++ -o lt-regexp lt-regexp.cc -I/usr/include/libxml2 -I/home/fran/local/include/lttoolbox-3.2 -L/home/fran/local/lib -llttoolbox3 -llibxml2
*/
#include <cwchar>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cerrno>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <set>
#include <lttoolbox/ltstr.h>
#include <lttoolbox/lt_locale.h>
#include <lttoolbox/transducer.h>
#include <lttoolbox/alphabet.h>
#include <lttoolbox/state.h>
#include <lttoolbox/regexp_compiler.h>
#include <lttoolbox/match_exe.h>
#include <lttoolbox/match_state.h>
#include <lttoolbox/xml_parse_util.h>
wstring ws(char *arg)
{
wchar_t buf[1024];
memset(buf, '\0', 1024);
size_t num_chars = mbstowcs(buf, arg, strlen(arg));
wstring ws(buf, num_chars);
return ws;
}
bool match(Transducer t, wstring str, Alphabet a)
{
map<int, int> finals;
for(int i = 0; i < t.size(); i++)
{
if(!t.isFinal(i))
{
continue;
}
finals[i] = i;
}
MatchExe me(t, finals);
MatchState ms;
ms.clear();
ms.init(me.getInitial());
for(wstring::iterator it = str.begin(); it != str.end(); it++)
{
wcout << ms.size() << " " << *it << endl;
ms.step(a(*it, *it));
}
int val = ms.classifyFinals(me.getFinals());
fwprintf(stdout, L"%d\n", val);
if(val != -1)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
Alphabet alphabet;
Transducer t;
RegexpCompiler re;
bool matched;
LtLocale::tryToSetLocale();
if(argc < 3)
{
wcout << L"Utilisation : lt-regexp <pattern> <chaîne à chercher>" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
FILE *output = stdout;
wstring pattern = ws(argv[1]);
wstring s = ws(argv[2]);
re.initialize(&alphabet);
re.compile(pattern);
t = re.getTransducer();
t.minimize();
t.show(alphabet, output);
matched = match(t, s, alphabet);
wcout << endl << pattern << " " << s << endl;
}